Crosslinking reagents are molecules containing two or more reactive ends capable of chemically binding to specific functional groups (primary amines, sulphydryl, etc.) via a covalent bond.
Crosslinking reagents are suitable for conjugating biomolecules (proteins, peptides, nucleic acids and hormones) to each other or to any molecular group that adds useful properties such as drugs, radionuclides, toxins, fluorophores, photoprobes, inhibitors, enzymes and ligands.
Their use is useful for the stabilisation of structures where protein-protein, protein-peptide or peptide/protein-small molecule interactions occur, in order to facilitate the identification of relationships between neighbouring proteins, ligand-receptor interactions, three-dimensional protein structures and molecular associations in cell membranes.
Likewise, they can also be used to modify nucleic acids, drugs and solid surfaces, and in the preparation of antibody-enzyme conjugates and immunotoxins.
Crosslinkers are used in a wide range of applications in the fields of drug discovery, assay development and pharmaceutical synthesis, for:
- the determination of protein structure and/or function
- the immobilisation of proteins or other biomolecules
- biomolecule-biomolecule conjugation in general
- drug-antibody conjugation
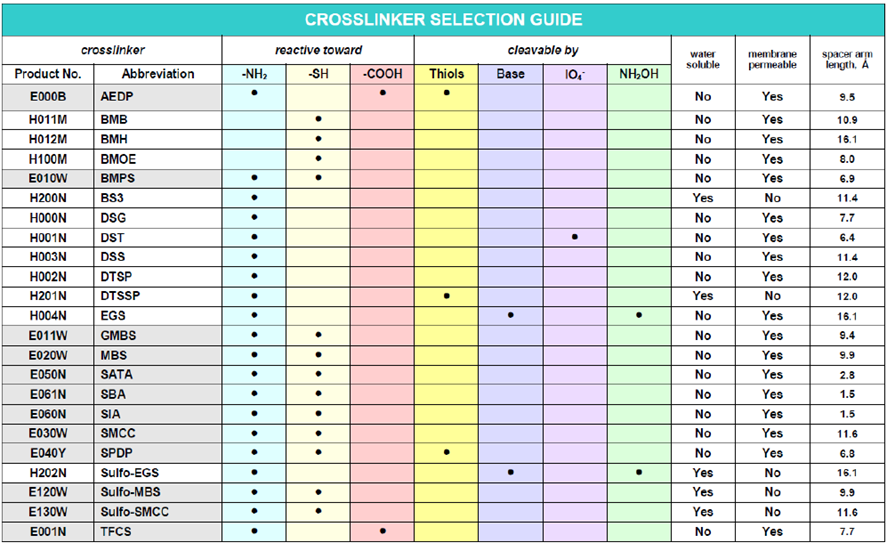
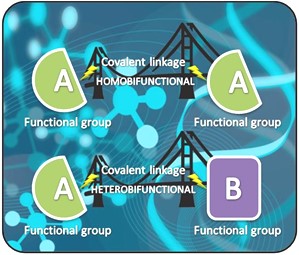
Crosslinking reagents can be classified into two macrocategories: homobifunctional and heterobifunctional, depending on whether they have two identical or different reactive groups at the end. Unlike homobifunctional crosslinking reagents, which merely facilitate the conjugation of molecules in one phase, heterobifunctional crosslinking reagents allow conjugations in two phases.
In addition to homobifunctional or heterobifunctional reactivity, the following properties are essential for the choice of crosslinker:
- Chemical specificity (amino, thiol, etc.)
- Length of the spacer arm
- Water solubility and membrane permeability
- Reversible or irreversible cross-link
- Possibility of two-step cross-linking
Some common examples of homobifunctional amine-amine crosslinkers include, among others:
- DSS, suitable for receptor ligand crosslinking
- DST, used for applications where crosslink cleavage is required while keeping the disulphide bonds of the protein intact
- DSP, ideally used for crosslinking intracellular proteins prior to cell lysis and immunoprecipitation, as well as for fixing protein interactions prior to the identification of weak or transient protein interactions
Cyanagen also manufactures and sells these reagents in customised and bulk forms for industrial uses.
For further information and quotations, please send an e-mail to: contact_us@cyanagen.com